-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
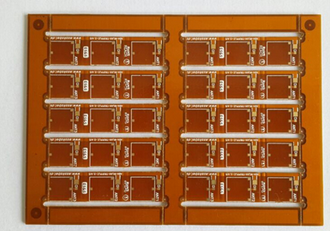
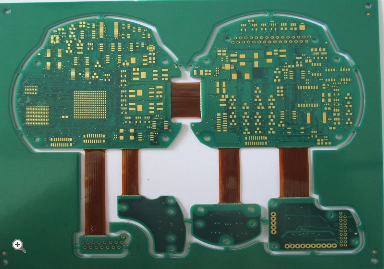
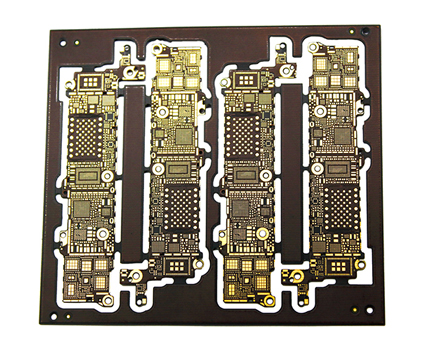
Rigid Flex PCBs A Game Changer For Space Constrained Designs Merging Robust Construction With Bendable Circuitry
In the relentless pursuit of miniaturization and enhanced functionality within modern electronics, designers are perpetually challenged by the constraints of physical space. From the sleek contours of wearable devices and foldable smartphones to the densely packed avionics of aircraft and the intricate instrumentation of medical implants, the demand for circuits that can conform to unconventional shapes without sacrificing reliability has never been greater. Enter Rigid-Flex PCBs, a transformative technology that is redefining the boundaries of electronic design. By seamlessly merging the durability and component support of traditional rigid boards with the dynamic, bendable nature of flexible circuits, Rigid-Flex PCBs offer a compelling solution for space-constrained applications. This hybrid approach is not merely an incremental improvement but a genuine game-changer, enabling robust construction and three-dimensional packaging that was previously unattainable, thereby opening new frontiers in product innovation and performance.
The Hybrid Architecture: Uniting Strength and Flexibility
At its core, a Rigid-Flex PCB is an integrated circuit board comprising multiple layers of flexible circuit substrates attached to one or more rigid boards. The flexible layers are typically made from polyimide, a material renowned for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand repeated flexing. These layers are permanently laminated to the rigid sections, which are usually constructed from standard FR-4 material, creating a single, unified structure.
The interconnection between the rigid and flexible areas is achieved through a sophisticated plating process, ensuring a continuous, reliable electrical path without the need for connectors, cables, or solder joints at these critical junctures. This monolithic construction eliminates many of the failure points associated with traditional board-to-board connections. The rigid sections provide stable platforms for mounting heavy components, connectors, and chips, while the flexible "hinges" allow the assembly to bend, fold, or twist to fit into uniquely shaped enclosures, effectively turning a two-dimensional circuit into a three-dimensional one.
Revolutionizing Design for Space-Constrained Applications
The primary advantage of Rigid-Flex technology lies in its unparalleled ability to save space and weight. In applications like drones, satellites, or military communications equipment, every cubic millimeter and gram is critical. By eliminating discrete wiring harnesses, connectors, and the associated mounting hardware, Rigid-Flex designs achieve a dramatic reduction in assembly volume. The circuits can be folded or rolled to occupy the exact available space, leading to more efficient use of the product's internal geometry.
This capability is revolutionary for consumer electronics as well. Modern smartphones, for instance, pack an immense amount of functionality into a slim profile. Rigid-Flex PCBs allow for the stacking of components and the routing of connections around batteries, cameras, and other internal modules in three dimensions. Similarly, in wearable health monitors or advanced hearing aids, the circuit can conform to the curves of the human body, ensuring a comfortable fit while maintaining a robust internal structure. This 3D packaging freedom allows engineers to design more compact, lighter, and ultimately more reliable end products.
Enhanced Reliability and Durability
Beyond space savings, the inherent construction of Rigid-Flex PCBs delivers superior reliability. Traditional designs that rely on soldered connectors and cabling between multiple rigid boards are susceptible to failure from vibration, mechanical shock, and thermal cycling. Solder joints can crack, and connectors can become loose over time. In a Rigid-Flex assembly, the flexible interconnects are an integral part of the board, withstanding significant dynamic flexing and harsh environmental conditions.
This robustness is paramount in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications where electronics are subjected to extreme temperatures, constant vibration, and moisture. The reduction in interconnection points directly correlates to a lower probability of failure. Furthermore, the assembly process is simplified as a single Rigid-Flex board replaces multiple interconnected parts, reducing human error during manufacturing and improving overall product yield and long-term field performance.
Streamlined Assembly and Cost Considerations
While the initial unit cost of a Rigid-Flex PCB can be higher than that of a traditional set of rigid boards and cables, the total cost of ownership often tells a different story. The simplified assembly process—involving fewer components to purchase, inventory, and solder—lowers labor costs and minimizes opportunities for defects. The integrated design also allows for automated assembly and testing as a single unit, increasing production efficiency.
Moreover, the improved reliability translates into lower warranty and repair costs over the product's lifecycle. For high-reliability industries, this reduction in potential field failures is invaluable. The design also allows for easier testing and prototyping of the complete electronic sub-system before final enclosure design is locked, potentially speeding up time-to-market. As manufacturing techniques advance and volumes increase, the cost premium for Rigid-Flex technology continues to decrease, making it accessible for a broader range of applications.
Driving Innovation in Next-Generation Products
Rigid-Flex PCB technology is not just solving existing design problems; it is actively enabling new product categories and functionalities. The development of foldable display devices is a prime example, where the main circuitry must bend reliably at a specific hinge point thousands of times. Advanced medical devices, such as implantable sensors or endoscopic capsules, leverage Rigid-Flex designs to be both minimally invasive and highly functional.
In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), where sensors are embedded into everyday objects with irregular forms, Rigid-Flex PCBs provide the necessary adaptability. Looking forward, as electronics continue to converge with mechanical systems in areas like soft robotics and conformal antennas, the ability to embed robust, bendable circuitry will be a fundamental enabler. The technology empowers designers to think beyond the flat board, envisioning electronics that are organic to the product's form and function.
In conclusion, Rigid-Flex PCBs represent a paradigm shift in electronic packaging. By masterfully merging robust construction with bendable circuitry, they provide an elegant and powerful answer to the dual challenges of space constraints and reliability demands. As electronic devices become ever more sophisticated and integrated into our lives and environments, the role of Rigid-Flex technology as a critical enabler for innovation is set to grow, solidifying its status as a true game-changer in modern electronic design.
REPORT