-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
Other Consumer Electronics
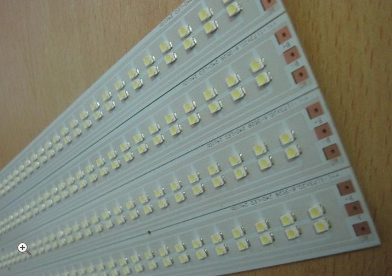
Your Best Choice for LED PCB Assembly
Unmatched Expertise and Experience
Our team comprises highly skilled engineers and technicians with years of experience in LED PCB assembly. We possess in-depth knowledge of various LED technologies, including surface mount technology (SMT), through-hole technology (THT), and hybrid assemblies. This diverse expertise enables us to handle projects of any complexity, from simple LED indicator boards to intricate high-power LED lighting systems. We stay abreast of the latest advancements in LED technology and manufacturing techniques, ensuring that we consistently deliver cutting-edge solutions.
Furthermore, our experience extends across a wide range of industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, industrial lighting, and medical devices. This broad exposure allows us to adapt our approach to meet the specific requirements of different applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in diverse environments. We understand the unique challenges each industry presents, and our solutions are tailored to overcome these challenges effectively.
State-of-the-Art Manufacturing Facilities
Our commitment to excellence extends to our state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities. We utilize advanced equipment and technologies to ensure precision and efficiency in every stage of the assembly process. Our facilities are equipped with high-speed pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and automated optical inspection (AOI) systems, guaranteeing superior quality control and minimizing errors. This investment in advanced technology allows us to handle high-volume production runs while maintaining the highest standards of accuracy and consistency.
Beyond the equipment, we maintain a meticulously clean and controlled environment to prevent contamination and ensure the longevity of your LED products. Our rigorous quality control procedures are implemented at every step, from incoming material inspection to final product testing, guaranteeing that only the highest quality components and assemblies leave our facility. This commitment to quality control translates to reduced field failures and increased customer satisfaction.
Comprehensive Services and Customized Solutions
We provide a comprehensive range of services, going beyond simple PCB assembly. Our services include design assistance, component sourcing, testing and quality control, and even after-sales support. We work closely with our clients throughout the entire process, from initial concept to final product delivery, ensuring seamless collaboration and transparent communication. We believe in a collaborative approach, where we leverage our expertise to help our clients optimize their designs and achieve their project goals.
We understand that every project is unique. That's why we offer customized solutions tailored to meet your specific requirements. Whether you need a small batch of prototypes or a large-scale production run, we can adapt our processes to accommodate your needs. Our flexibility and responsiveness are key differentiators, ensuring that we consistently deliver on time and within budget.
Commitment to Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Our ultimate goal is to deliver exceptional quality and unparalleled customer satisfaction. We are committed to exceeding your expectations at every stage of the process. Our ISO 9001 certification serves as a testament to our unwavering dedication to quality management systems. We continually strive for improvement, investing in new technologies and training programs to maintain our leadership position in the industry.
We believe that strong customer relationships are the cornerstone of our success. We are always available to answer your questions, provide technical support, and address any concerns you may have. Our responsive and proactive approach ensures that you are well-informed throughout the entire process and confident in our ability to deliver exceptional results.

Reliable LED PCB Assembly Solutions Now
Superior Component Selection and Quality Control
The foundation of any reliable LED PCB assembly lies in the quality of its components. Selecting high-quality LEDs with consistent lumen output, color temperature, and lifespan is paramount. Reputable manufacturers provide detailed specifications and certifications, ensuring that components meet rigorous industry standards. This initial selection process significantly impacts the overall reliability and performance of the final assembly. Furthermore, a robust quality control system is essential, implementing rigorous inspection procedures at every stage of the component procurement and assembly process. This involves thorough testing for defects, ensuring that only components meeting the highest standards are integrated into the PCB.
Beyond the LEDs themselves, other components like resistors, capacitors, and drivers also require careful selection and testing. The proper selection of these components ensures optimal current regulation, preventing overheating and extending the lifespan of the LEDs. Ignoring this crucial step can lead to premature failure and compromise the overall reliability of the assembly. Implementing a multi-stage quality control process, including visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), and functional testing, is crucial to identify and eliminate any defects before the assembly reaches the end user.
Advanced Soldering Techniques and Equipment
Precise and efficient soldering is critical for reliable LED PCB assembly. The heat sensitivity of LEDs demands a delicate approach, avoiding thermal stress that could damage the components. Advanced soldering techniques, such as reflow soldering, utilize controlled temperature profiles to minimize the risk of damage while ensuring strong and consistent solder joints. This ensures reliable electrical connections and optimal heat dissipation, vital for preventing overheating and extending the operational lifespan of the LEDs.
Investing in state-of-the-art equipment, such as automated pick-and-place machines and reflow ovens with precise temperature control, is crucial for consistent and high-quality soldering. These machines ensure accurate placement of components and uniform heating, minimizing defects and ensuring consistent performance across all assemblies. Regular maintenance and calibration of this equipment are also essential to guarantee long-term reliability and accuracy.
Design for Reliability (DFR) Principles
Designing for reliability (DFR) incorporates principles that enhance the lifespan and performance of the final product. This goes beyond component selection and soldering techniques, encompassing the entire design process. Careful consideration of thermal management is crucial for LEDs, which generate significant heat. The PCB layout needs to facilitate efficient heat dissipation, preventing overheating and potential failure. This might involve the use of heat sinks, copper planes, and strategic component placement.
DFR also involves selecting appropriate materials for the PCB itself, considering factors such as thermal conductivity and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. Robust PCB design further involves using appropriate circuit protection mechanisms, such as surge protection devices, to safeguard the LEDs from voltage spikes and other potential damage. Implementing DFR principles from the outset reduces the likelihood of field failures, resulting in more reliable and long-lasting products.
Testing and Validation
Comprehensive testing is essential to ensure the reliability of LED PCB assemblies. This goes beyond simple visual inspection and involves functional testing to verify that the assembly operates according to specifications under various conditions. Environmental testing, simulating real-world conditions like temperature extremes and humidity, helps identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities. These tests ensure that the assembly can withstand the rigors of its intended application, maintaining optimal performance over its operational lifespan.
Implementing rigorous testing procedures, including burn-in tests, helps to identify early failures and ensure that only high-quality assemblies are shipped to customers. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of field failures and significantly reduces warranty claims, enhancing customer satisfaction and building brand reputation. Data collected during testing provides valuable feedback for continuous improvement, optimizing the assembly process and ensuring ongoing reliability.

Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control
Enhanced Edge Coverage and Uniformity
One of the key strengths of Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control lies in its ability to deliver exceptionally uniform plating thickness across the entire board, including the often-neglected edges. This is achieved through a combination of sophisticated algorithms and advanced process control techniques. These algorithms analyze the PCB geometry and plating parameters in real-time, dynamically adjusting the plating process to compensate for variations in current distribution and edge effects. This ensures that even the most intricate board geometries receive consistent plating, minimizing the risk of thin spots or uneven deposits that can lead to failures.
Furthermore, the system's flexibility extends to handling a wide range of board materials and plating types. Whether working with copper, nickel, gold, or other common plating materials, the control system adapts its parameters to optimize the plating process for each specific application. This adaptability is crucial for manufacturers dealing with diverse product lines and varying material specifications. The consistency of results achieved reduces the need for time-consuming manual adjustments and inspections, streamlining the overall manufacturing process.
Improved Process Control and Monitoring
Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control incorporates advanced monitoring and feedback mechanisms to ensure optimal process control. Real-time data acquisition and analysis provide continuous feedback on key parameters such as current density, plating rate, and solution chemistry. This allows for immediate detection and correction of any deviations from the desired parameters, minimizing the likelihood of defects. The system's intuitive user interface presents this data in a clear and concise manner, facilitating quick troubleshooting and operator intervention when necessary.
Beyond real-time monitoring, the system also incorporates historical data logging and analysis capabilities. This allows manufacturers to track trends, identify potential process improvements, and proactively address any emerging issues. This data-driven approach contributes to continuous process optimization, leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste. The comprehensive data logging and reporting features also enhance traceability and compliance with industry standards.
Reduced Waste and Improved Efficiency
The precise control offered by Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control contributes significantly to reduced waste. By eliminating the need for excessive plating due to uneven deposition, the system minimizes the consumption of precious metals and chemicals. This not only reduces manufacturing costs but also contributes to a more environmentally responsible manufacturing process. Furthermore, the consistent plating results reduce the need for rework and scrap, further enhancing overall efficiency.
The automated nature of the control system also streamlines the plating process, minimizing the need for manual intervention. This reduces labor costs and frees up personnel for other tasks. The reduction in inspection and rework time further contributes to faster turnaround times and increased production throughput. The overall impact is a more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing operation.
Enhanced Product Reliability and Quality
The ultimate benefit of Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control is the significant enhancement in product reliability and quality. By ensuring consistent and uniform plating, the system minimizes the risk of defects such as delamination, corrosion, and solderability issues. This leads to improved product performance and increased lifespan. The reduced defect rate also contributes to higher yields and lower warranty costs.
In today's competitive market, delivering high-quality products consistently is paramount. Reliable Flexible Edge Plating Board Control empowers manufacturers to meet these demands by providing a robust and reliable solution for achieving superior plating results. The improved edge coverage, precise control, reduced waste, and enhanced product reliability all contribute to a significant return on investment, making it a compelling solution for PCB manufacturers seeking to optimize their processes and enhance their product offerings.

Innovative Flexible Edge Plating Solutions
Enhanced Flexibility and Conformability
Traditional edge plating methods, often employed with rigid PCBs, rely on processes unsuitable for flexible substrates. These processes can damage delicate flexible materials, leading to cracks and delamination. Innovative flexible edge plating solutions address this challenge by utilizing gentler techniques that maintain the integrity of the flexible substrate. Electrodeposition processes, for instance, have been refined to allow for thinner, more conformal plating layers, minimizing stress on the flexible material. The use of specialized plating baths and tailored current densities contributes to superior adhesion between the plating and the substrate, ensuring long-term reliability.
Furthermore, advancements in substrate materials have played a crucial role. The development of high-performance flexible substrates, such as polyimide films and flexible metals, has expanded the possibilities for flexible edge plating. These materials offer superior flexibility and resilience, enabling the creation of complex, three-dimensional structures while maintaining the structural integrity of the plated edges.
Improved Electrical Conductivity and Reliability
The quality of the edge plating directly impacts the electrical performance of the flexible circuit. Innovative solutions prioritize achieving high electrical conductivity and reliable connections. This is achieved through careful control of the plating process parameters, ensuring a uniform and dense plating layer with minimal porosity. The choice of plating material is also critical; materials like gold and nickel are favored due to their excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and solderability.
Minimizing contact resistance at the interface between the plated edge and the connector is paramount. Advanced surface finishing techniques, such as electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), are commonly employed to create a smooth, low-resistance surface. These techniques not only enhance electrical performance but also improve the durability and reliability of the connections, ensuring consistent performance throughout the device's lifespan.
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
The success of any technology hinges on its ability to be scaled for mass production while remaining cost-effective. Innovative flexible edge plating solutions are designed with scalability in mind. Many processes are readily adaptable to automated manufacturing techniques, allowing for high-volume production while maintaining consistent quality. This is particularly crucial for applications where large quantities of flexible circuits are required, such as in wearable electronics or smart packaging.
The cost-effectiveness of these solutions is also a key consideration. While advanced materials and processes may initially appear expensive, advancements in automation and material optimization have led to significant reductions in production costs. This makes flexible edge plating a viable option for a wider range of applications, fostering innovation and driving market growth.
Materials Compatibility and Environmental Considerations
The selection of materials used in flexible edge plating is crucial not only for electrical performance but also for environmental compatibility. Many innovative solutions prioritize the use of environmentally friendly materials and processes. This includes the development of lead-free plating options, minimizing the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal. Furthermore, the development of techniques that minimize waste generation and improve resource efficiency is an ongoing priority.
Compatibility with various substrate materials is another vital aspect. Innovative solutions need to be adaptable to a range of flexible substrates, allowing for design flexibility and the creation of diverse flexible electronic devices. This broad material compatibility is essential for meeting the varied requirements of different applications.
Future Trends and Applications
The field of flexible edge plating is constantly evolving, driven by the ever-increasing demand for flexible electronics. Future trends include the development of even more flexible and thinner plating layers, allowing for greater conformability and integration into complex geometries. Research is also focusing on the development of new plating materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity, durability, and biocompatibility.
The applications for innovative flexible edge plating solutions are vast and continue to expand. Beyond the aforementioned examples, these solutions are playing a crucial role in the development of advanced medical devices, flexible sensors for environmental monitoring, and high-performance antennas for communication systems. As technology advances, the demand for flexible electronics will only continue to grow, driving further innovation in the field of flexible edge plating and opening up exciting new possibilities for future applications.
REPORT



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































