-
 Agriculture
Agriculture
-
 Health-Care
Health-Care
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Construction-Real-Estate
Construction-Real-Estate
-
 Tools-Hardware
Tools-Hardware
-
 Home-Garden
Home-Garden
-
 Furniture
Furniture
-
 Luggage-Bags-Cases
Luggage-Bags-Cases
-
 Medical-devices-Supplies
Medical-devices-Supplies
-
 Gifts-Crafts
Gifts-Crafts
-
 Sports-Entertainment
Sports-Entertainment
-
 Food-Beverage
Food-Beverage
-
 Vehicles-Transportation
Vehicles-Transportation
-
 Power-Transmission
Power-Transmission
-
 Material-Handling
Material-Handling
-
 Renewable-Energy
Renewable-Energy
-
 Safety
Safety
-
 Testing-Instrument-Equipment
Testing-Instrument-Equipment
-
 Construction-Building-Machinery
Construction-Building-Machinery
-
 Pet-Supplies
Pet-Supplies
-
 Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
Personal-Care-Household-Cleaning
-
 Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
Vehicle-Accessories-Electronics-Tools
-
 School-Office-Supplies
School-Office-Supplies
-
 Packaging-Printing
Packaging-Printing
-
 Mother-Kids-Toys
Mother-Kids-Toys
-
 Business-Services
Business-Services
-
 Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
Commercial-Equipment-Machinery
-
 Apparel-Accessories
Apparel-Accessories
-
 Security
Security
-
 Shoes-Accessories
Shoes-Accessories
-
 Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
Vehicle-Parts-Accessories
-
 Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
Jewelry-Eyewear-Watches-Accessories
-
 Lights-Lighting
Lights-Lighting
-
 Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
Fabric-Textile-Raw-Material
-
 Fabrication-Services
Fabrication-Services
-
 Industrial-Machinery
Industrial-Machinery
-
 Consumer-Electronics
Consumer-Electronics
-
 Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
Electrical-Equipment-Supplies
-
 Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
Electronic-Components-Accessories-Telecommunications
-
 Home-Appliances
Home-Appliances
-
 Beauty
Beauty
-
 Chemicals
Chemicals
-
 Rubber-Plastics
Rubber-Plastics
-
 Metals-Alloys
Metals-Alloys
- Masonry Materials
- Curtain Walls & Accessories
- Earthwork Products
- Fireproofing Materials
- Heat Insulation Materials
- Plastic Building Materials
- Building Boards
- Soundproofing Materials
- Timber
- Waterproofing Materials
- Balustrades & Handrails
- Bathroom & Kitchen
- Flooring & Accessories
- Tiles & Accessories
- Door, Window & Accessories
- Fireplaces & Stoves
- Floor Heating Systems & Parts
- Stairs & Stair Parts
- Ceilings
- Elevators & Escalators
- Stone
- Countertops, Vanity Tops & Table Tops
- Mosaics
- Metal Building Materials
- Multifunctional Materials
- Ladders & Scaffoldings
- Mouldings
- Corner Guards
- Decorative Films
- Formwork
- Building & Industrial Glass
- Other Construction & Real Estate
- Wallpapers/Wall panels
- HVAC System & Parts
- Outdoor Facilities
- Prefabricated Buildings
- Festive & Party Supplies
- Bathroom Products
- Household Sundries
- Rain Gear
- Garden Supplies
- Household Cleaning Tools & Accessories
- Lighters & Smoking Accessories
- Home Storage & Organization
- Household Scales
- Smart Home Improvement
- Home Textiles
- Kitchenware
- Drinkware & Accessories
- Dinnerware, Coffee & Wine
- Home Decor
- Golf
- Fitness & Body Building
- Amusement Park Facilities
- Billiards, Board Game,Coin Operated Games
- Musical Instruments
- Outdoor Affordable Luxury Sports
- Camping & Hiking
- Fishing
- Sports Safety&Rehabilitation
- Ball Sports Equipments
- Water Sports
- Winter Sports
- Luxury Travel Equipments
- Sports Shoes, Bags & Accessories
- Cycling
- Other Sports & Entertainment Products
- Artificial Grass&Sports Flooring&Sports Court Equipment
- Scooters
- Food Ingredients
- Honey & Honey Products
- Snacks
- Nuts & Kernels
- Seafood
- Plant & Animal Oil
- Beverages
- Fruit & Vegetable Products
- Frog & Escargot
- Bean Products
- Egg Products
- Dairy Products
- Seasonings & Condiments
- Canned Food
- Instant Food
- Baked Goods
- Other Food & Beverage
- Meat & Poultry
- Confectionery
- Grain Products
- Feminie Care
- Hair Care & Styling
- Body Care
- Hands & Feet Care
- Hygiene Products
- Men's Grooming
- Laundry Cleaning Supplies
- Travel Size & Gift Sets
- Room Deodorizers
- Other Personal Care Products
- Pest Control Products
- Special Household Cleaning
- Floor Cleaning
- Kitchen & Bathroom Cleaning
- Oral Care
- Bath Supplies
- Yellow Pages
- Correction Supplies
- Office Binding Supplies
- Office Cutting Supplies
- Board Erasers
- Office Adhesives & Tapes
- Education Supplies
- Pencil Cases & Bags
- Notebooks & Writing Pads
- File Folder Accessories
- Calendars
- Writing Accessories
- Commercial Office Supplies
- Pencil Sharpeners
- Pens
- Letter Pad/Paper
- Paper Envelopes
- Desk Organizers
- Pencils
- Markers & Highlighters
- Filing Products
- Art Supplies
- Easels
- Badge Holder & Accessories
- Office Paper
- Printer Supplies
- Book Covers
- Other Office & School Supplies
- Stationery Set
- Boards
- Clipboards
- Stamps
- Drafting Supplies
- Stencils
- Electronic Dictionary
- Books
- Map
- Magazines
- Calculators
- Baby & Toddler Toys
- Educational Toys
- Classic Toys
- Dress Up & Pretend Play
- Toy Vehicle
- Stuffed Animals & Plush Toys
- Outdoor Toys & Structures
- Balloons & Accessories
- Baby Food
- Children's Clothing
- Baby Supplies & Products
- Maternity Clothes
- Kids Shoes
- Baby Care
- Novelty & Gag Toys
- Dolls & Accessories
- Puzzle & Games
- Blocks & Model Building Toys
- Toddler Clothing
- Baby Clothing
- Kids' Luggage & Bags
- Arts, Crafts & DIY Toys
- Action & Toy Figures
- Baby Appliances
- Hobbies & Models
- Remote Control Toys
- Promotional Toys
- Pregnancy & Maternity
- Hygiene Products
- Kid's Textile&Bedding
- Novelty & Special Use
- Toy Weapons
- Baby Gifts
- Baby Storage & Organization
- Auto Drive Systems
- ATV/UTV Parts & Accessories
- Marine Parts & Accessories
- Other Auto Parts
- Trailer Parts & Accessories
- Auto Transmission Systems
- Train Parts & Accessories
- Universal Parts
- Railway Parts & Accessories
- Auto Brake Systems
- Aviation Parts & Accessories
- Truck Parts & Accessories
- Auto Suspension Systems
- Auto Lighting Systems
- New Energy Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Steering Systems
- Wheels, Tires & Accessories
- Bus Parts & Accessories
- Auto Performance Parts
- Cooling System
- Go-Kart & Kart Racer Parts & Accessories
- Air Conditioning Systems
- Heavy Duty Vehicle Parts & Accessories
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Auto Body Systems
- Auto Engine Systems
- Container Parts & Accessories
- Motorcycle Parts & Accessories
- Refrigeration & Heat Exchange Equipment
- Machine Tool Equipment
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Agricultural Machinery & Equipment
- Apparel & Textile Machinery
- Chemical Machinery
- Packaging Machines
- Paper Production Machinery
- Plastic & Rubber Processing Machinery
- Industrial Robots
- Electronic Products Machinery
- Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- Woodworking Machinery
- Home Product Manufacturing Machinery
- Machinery Accessories
- Environmental Machinery
- Machinery Service
- Electrical Equipment Manufacturing Machinery
- Industrial Compressors & Parts
- Tobacco & Cigarette Machinery
- Production Line
- Used Industrial Machinery
- Electronics Production Machinery
- Other Machinery & Industrial Equipment
- Camera, Photo & Accessories
- Portable Audio, Video & Accessories
- Television, Home Audio, Video & Accessories
- Video Games & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Accessories
- Electronic Publications
- Earphone & Headphone & Accessories
- Speakers & Accessories
- Smart Electronics
- TV Receivers & Accessories
- Mobile Phone & Computer Repair Parts
- Chargers, Batteries & Power Supplies
- Used Electronics
- VR, AR, MR Hardware & Software
- Projectors & Presentation Equipments
- Other Consumer Electronics
- Cables & Commonly Used Accessories
- Computer Hardware & Software
- Displays, Signage and Optoelectronics
- Discrete Semiconductors
- Wireless & IoT Module and Products
- Telecommunications
- Connectors, Terminals & Accessories
- Development Boards, Electronic Modules and Kits
- Circuit Protection
- Sensors
- Isolators
- Audio Components and Products
- Integrated Circuits
- Power Supplies
- Relays
- RF, Microwave and RFID
- Electronic Accessories & Supplies
- Passive Components
- PCB & PCBA
- Air Quality Appliances
- Home Appliance Parts
- Heating & Cooling Appliances
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Laundry Appliances
- Water Heaters
- Water Treatment Appliances
- Refrigerators & Freezers
- Personal Care & Beauty Appliances
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cleaning Appliances
- Second-hand Appliances
- Smart Home Appliances
- Other Home Appliances
- Energy Chemicals
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Basic Organic Chemicals
- Agrochemicals
- Admixture & Additives
- Catalysts & Chemical Auxiliary Agents
- Pigments & Dyestuff
- Coating & Paint
- Daily Chemicals
- Polymer
- Organic Intermediate
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Chemical Waste
- Biological Chemical Products
- Surface Treatment Chemicals
- Painting & Coating
- Chemical Reagents
- Flavor & Fragrance
- Non-Explosive Demolition Agents
- Other Chemicals
- Custom Chemical Services
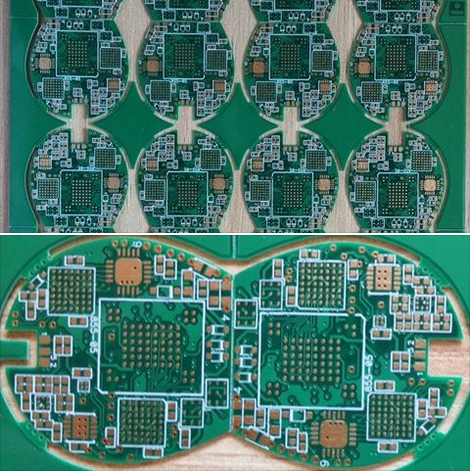
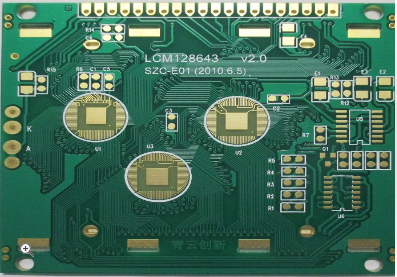
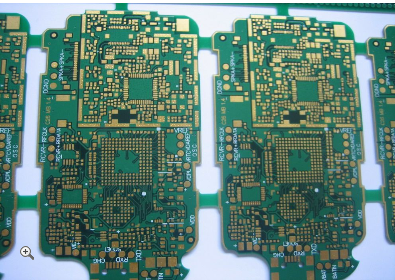
Innovative HDI PCB Design Enabling Higher Circuit Density And Improved Signal Integrity For Cutting Edge Applications
In the relentless pursuit of miniaturization and performance, the electronics industry stands at a pivotal juncture. Cutting-edge applications—from artificial intelligence accelerators and 5G/6G infrastructure to advanced medical implants and autonomous vehicles—demand unprecedented levels of functionality packed into ever-shrinking form factors. This relentless drive pushes conventional printed circuit board (PCB) technologies to their physical limits, creating bottlenecks in circuit density, signal speed, and thermal management. It is within this challenging landscape that Innovative High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCB design emerges not merely as an improvement, but as a fundamental enabler of next-generation technology. By leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and sophisticated design methodologies, HDI PCB design transcends traditional constraints, offering a pathway to achieve higher circuit density and superior signal integrity simultaneously. This article delves into the core principles and multifaceted advantages of innovative HDI design, exploring how it serves as the critical backbone for the most demanding electronic systems of today and tomorrow.
The Architectural Foundation: Core Principles of HDI Technology
At its heart, HDI technology is defined by its use of finer lines and spaces, smaller vias, and higher connection pad density than conventional PCBs. The foundational innovation lies in the use of microvias—laser-drilled holes typically less than 150 microns in diameter. Unlike traditional through-hole vias that penetrate the entire board, microvias can connect adjacent layers, allowing for more efficient use of internal real estate. This is often implemented in build-up structures, where layers are sequentially laminated and interconnected, creating a complex, high-density routing environment.
Furthermore, innovative HDI employs advanced structures like stacked and staggered microvias, and utilizes materials with superior dielectric properties. The shift from standard FR-4 to low-loss, high-frequency laminates is integral to this design philosophy. These materials exhibit a more stable dielectric constant (Dk) and lower dissipation factor (Df), which are crucial for maintaining signal integrity at multi-gigabit speeds. The combination of geometric precision and advanced material science forms the bedrock upon which the benefits of HDI are built, enabling designers to break free from the grid-based routing limitations of the past.
Unlocking Miniaturization: Achieving Higher Circuit Density
The most immediate impact of innovative HDI design is the dramatic increase in circuit density. By utilizing microvias and fine-line tracing, designers can route more connections in a given area, effectively allowing for more complex integrated circuits (ICs), particularly ball grid array (BGA) and chip-scale package (CSP) components, to be placed on a smaller board. This miniaturization is not just about making devices smaller; it is about adding enhanced functionality—more sensors, more processing cores, more memory channels—without increasing the physical footprint.
This density is achieved through the efficient use of the Z-axis, or the vertical space within the board. Traditional through-hole vias occupy space on every layer they pass through, creating "via keep-out" zones that block routing channels. Microvias, in contrast, only affect the layers they connect, freeing up valuable routing area on other layers. This allows for more signal layers to be packed into a thinner overall board profile. For portable consumer electronics, wearable devices, and aerospace systems, where every cubic millimeter counts, this capability is indispensable for meeting stringent size and weight requirements while boosting performance.
The Lifeline of High-Speed Design: Ensuring Superior Signal Integrity
As data rates soar into the tens of gigabits per second, maintaining signal integrity becomes the paramount challenge. Innovative HDI design directly addresses the three primary enemies of high-speed signals: impedance discontinuities, crosstalk, and signal loss. The use of microvias significantly reduces the parasitic capacitance and inductance associated with via stubs in traditional through-holes, leading to fewer impedance mismatches and reflections that can distort digital signals.
Moreover, the finer geometries and controlled dielectric materials enable more precise impedance control across the entire signal path. Designers can implement tightly coupled differential pairs and optimize trace geometries to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between adjacent signals. The improved layer-to-layer registration inherent in HDI manufacturing processes ensures that return paths for high-speed signals are consistent and well-defined, which is critical for managing electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). Consequently, systems benefit from cleaner signals, lower bit-error rates, and the ability to reliably transmit data over longer distances on the board, which is essential for the integrity of high-speed serial links like PCI Express, DDR memory buses, and SerDes channels.
Enhancing Reliability and Thermal Performance
The benefits of innovative HDI design extend beyond density and speed to encompass enhanced reliability and thermal management. The smaller microvias, due to their reduced aspect ratio (the ratio of depth to diameter), are more reliably plated during manufacturing, resulting in fewer defects and improved long-term durability under thermal cycling stress. This increased structural robustness is vital for applications in automotive, industrial, and aerospace environments where reliability is non-negotiable.
Thermally, the high-density component placement enabled by HDI can create localized hotspots. However, the design methodology itself provides solutions. HDI boards facilitate the integration of embedded thermal management features, such as thermal vias—arrays of microvias placed directly under high-power components to conduct heat into internal ground planes or to external heatsinks. Additionally, the ability to use thinner dielectrics and more copper layers improves the overall thermal conductivity of the board stack-up, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively. This proactive thermal design prevents performance throttling and extends the operational lifespan of sensitive components.
Empowering Cutting-Edge Applications
The convergence of higher density, superior signal integrity, and improved reliability uniquely positions innovative HDI PCB design as the platform for revolutionary applications. In telecommunications, it is the foundation of massive MIMO antennas and millimeter-wave modules for 5G/6G networks, where countless antenna elements and RF front-ends must be integrated into compact arrays. For artificial intelligence and high-performance computing, HDI enables the dense interconnects required between GPUs, TPUs, and high-bandwidth memory (HBM), overcoming the "memory wall" and facilitating faster data processing.
In the medical field, HDI technology allows for the development of sophisticated implantable devices and miniaturized diagnostic equipment, such as capsule endoscopes and advanced hearing aids, which require extreme reliability and minimal size. The automotive sector leverages HDI for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), where sensor fusion from LiDAR, radar, and cameras demands robust, high-speed PCBs that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Each of these domains relies on the synergistic advantages of HDI to turn conceptual breakthroughs into tangible, market-ready technologies, pushing the boundaries of what is electronically possible.
REPORT